The Ideal Gas Law for a Gas Mixture. Where P is the pressure V is the volume n is the molar amount R is the gas constant and T is the temperature in absolute.
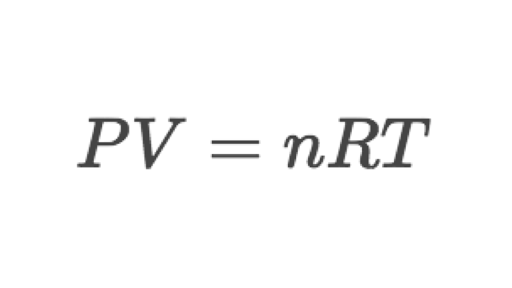
What Is The Ideal Gas Law Article Khan Academy
Gases are described in terms of their pressure and temperature and the.

. Amagats law or the Law of Partial Volumes describes the behaviour and properties of mixtures of ideal as well as some cases of non-ideal gases. P ρR T pressure DensitymV temperature degree Kelvin gas constant its value depends on the gas considered ESS55 Prof. Why or why not.
The ideal gas law mathematically describes the relationship between pressure temperature volume and molar amount for gases that are well approximated as ideal gases. Consider two gases A and B of volumes V A and V B respectively mixed together to. Amagats law states that the total volume of an ideal gas mixture is equivalent to the addition of the volumes of all discrete components present in the gas mixture such that the total pressure and temperature of gas mixture remain unchanged.
An ideal gas contains molecules of a negligible size that have an average molar kinetic energy that depends only on temperature. Amagats law states that the extensive volume V Nv of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of volumes V i of the K component gases if the temperature T and the pressure p remain. Even mixtures of gases such as air can be described as a mixture of ideal gases.
With P absolute pressure of the gas V volume of the gas n quantity of the gas in moles T absolute temperature of the gas R perfect gas constant. Sections 104 106 of Brown LeMay Bursten and Murphy. This states that the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the constituent gases.
You want to find the density using the truncated virial equation of state use Equation 53-3 in the textbook. Silver oxide can be decomposed to yield silver metal and oxygen gas according to the equation below. The perfect gas model obeys the ideal gas equation.
This generates the ideal gas law and the constant R is known as the gas constant. Jin-Yi Yu Gas Constant The ideal gas law can be applied to the combination of atmospheric gases or to individual gases. Is this mixture well-modeled by the ideal gas law.
Of use in chemistry and thermodynamics Amagats law states that the volume Vm of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of volumes Vi of the K component gases if the temperature T and the pressure p remain the same. A mixture of ideal gas adopts the same behavior as a pure ideal gas the equation of state of the ideal gas is thus still valid for the whole gas. Intermolecular forces and molecular size are not considered by the Ideal Gas Law.
Is this mixture well-modeled by the ideal gas law. Many real gases are well described as an ideal gas such as nitrogen oxygen hydrogen and the noble gases. The simplest model of a gas consists of many randomly moving point particles which do not interact with each other.
Equation 1 can be simplified as. You want to find the density using the truncated virial equation of state use Equation 53-3 in the textbook. The partial pressure is defined as the pressure each gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture at the mixtures temperature.
Z is equal to 1 for the ideal gas law. D R T P z H H H 2 2 2 1. Is this mixture well-modeled by the ideal gas law.
Why or why not. Ideal-Gas Mixtures All gases that comprise a mixture at a high temperature and low pressure relative to the critical point values of individual gases can be treated as ideal gases GibbsDalton law the properties of a gas are not influenced by the presence of other gases and each gas component in the mixture behaves as ideal gas if it exists alone at the mixture temperature Tm. P absolute pressure in the mixture Nm 2 lbft 2 V volume of the mixturem 3 ft 3 m m mass of the mixture kg lb R m the individual gas constant for the mixture Jkg K ft lbslugs o R T absolute temperature in the mixture o K o.
It is of use in chemistry and thermodynamics. The hydrogen gas constant R H 2 is 4124 JkgK. The Ideal Gas Law applies to ideal gases.
Analysis of a Chemical Mixture Using the Ideal Gas Law PRELAB. 1 In this model heat capacity is temperature dependent. The Ideal Gas Law for a perfect or ideal gas adapted for a gas mixture.
The value of gas constant for the particular gas under. Why or why not. Without solving write the equation to solve for the inlet mixtures density using the virial equation of state in terms of R T P B and molecular weight.
You want to find the density using the truncated virial equation of state use Equation 53-3 in the textbook. Without solving write the equation to solve for the inlet mixtures density using the virial equation of state in terms of R T P B and molecular weight. Perfect Gas law Avogadro Law.
The hydrogen co-density d H2 is about 00645 molcm3 or 129 kgm3. The Ideal Gas Law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. Mixture obey the following ideal gas equation.
You conduct this reaction with an unknown mass of Ag 2O and collect 812 mL of O 2. Without solving write the equation to solve for the inlet mixtures density using the virial equation of state in terms of R T P B and molecular weight. 2 Journal of Thermodynamics The state of an ideal gas is modeled using the ideal gas equation pvRT.
Amagats law or the Law of Partial Volumes of 1880 describes the behavior and properties of mixtures of ideal as well as some cases of non-ideal gases. P V m m R m T 1 where. 2 The AN-EOS accounts for the finite volume occupied by the gas molecules but it neglects the effects of.
It is also referred to as the law of volume fraction.

The Ideal Gas Law And Kinetic Theory Of Gases Ppt Video Online Download
The Ideal Gas Law Equation Constant Chemtalk

Ideal Gas Law Calculator Pressure Volume Temperature Amount Thermodynamics Heat Online Unit Converters
0 Comments